Eternal fires are fires that are born from natural gas veins or are born from human intervention and burn for a long time without being extinguished.
1. Eternal Flame Falls, Shale Creek Preserve, New York, USA
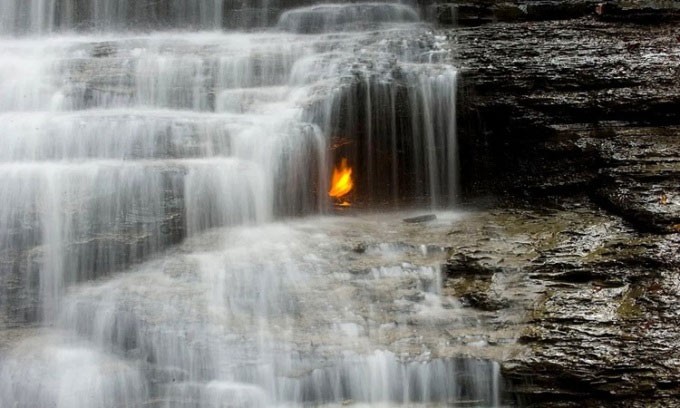

The 8-inch-tall eternal flame that has been burning for thousands of years, nestled in a small cave behind the 35-foot-tall Eternal Flame Falls in the Shale Creek Preserve, is one of the most famous eternal flames in the world.
Researchers have yet to determine the source of the eternal flame’s constant fuel supply. The theory is that some geological process has been steadily releasing natural gas from shale rock at a depth of 400m, fueling the flame.
The small fire can be observed most of the year and even burns in winter when the waterfall freezes. However, occasionally it may go out and need to be re-lit.
2. Yanartas, Olympos Valley, Türkiye

Yanartas, located on the Chimaera Mountain in the Olympos Valley in modern-day Antalya, Türkiye, is home to dozens of small, natural eternal flames that have been burning for over 2.5 millennia. At night, the area looks like hell on Earth.
3. Erta Ale, Ethiopia
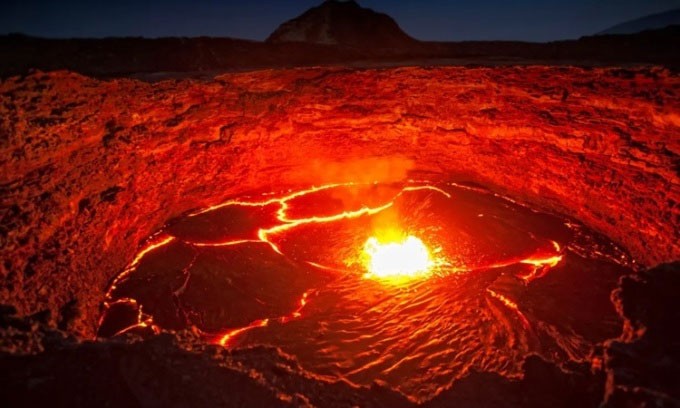

Erta Ale is a 613m-high shield volcano located in the Afar Basin of Ethiopia. It is notable for its nearby active lava lake, which has earned it the nickname "the Door to Hell". Erta Ale's lava lake was discovered in 1906.
4. Yanar Dağ, Azerbaijan
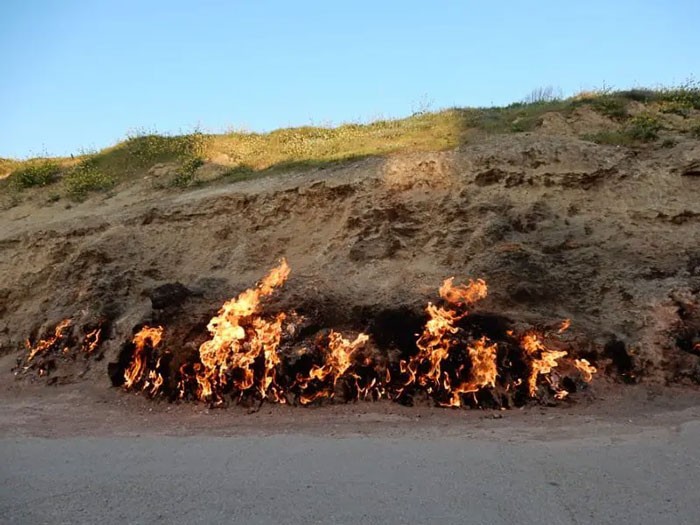

Yanar Dağ in Azerbaijan, located in the Lesser Caucasus Mountains, Azerbaijan, is a natural eternal fire. Yanar Dag burns with natural gas seeping from the porous sandstone on the hillside above Absheron Bay, reaching 2.74 m high.
5. Darvaza gas crater, Turkmenistan
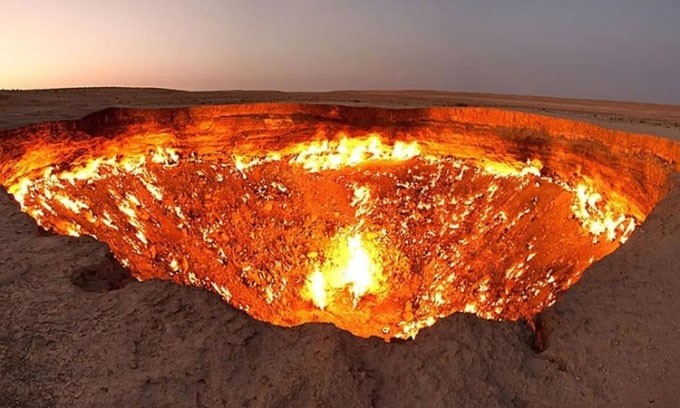

The Darvaza Crater in Turkmenistan has been burning continuously for more than 50 years and has been nicknamed the Door to Hell.
This eternal flame was created by human hands. In the 1970s, Soviet petroleum engineers discovered a huge gas field, and drilling operations in the area led to an underground collapse that caused large amounts of methane gas to begin spewing to the surface. The engineers decided to burn the gas to prevent the methane from accumulating to unsafe levels.